What is the difference between rheumatic diseases? How to detect problems in time?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic inflammatory disease of the connective tissue that affects the small joints (elbows, knees, hands and feet) in an erosive fashion. As a result, the bone is worn away and deformed afterwards. Over time, the symptoms of the disease get worse and lead to disability. About 60 million people around the world suffer from this disease. The disease is more commonly affected in women, with an average age of 30 to 35 years.
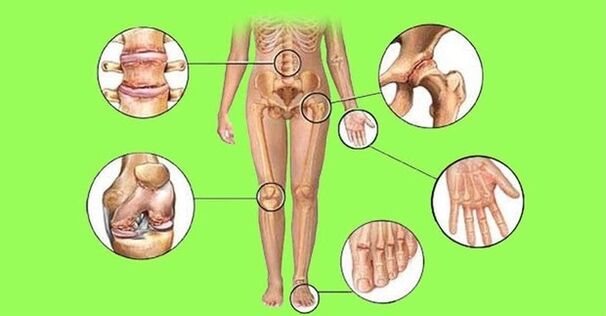
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease that affects the cartilage tissue of the ankle, knee, shoulder, hip, and foot joints. The progressive form flows into osteoarthritis, creating limitations on a person's range of motion. The disease can develop in two symmetrical joints at the same time. Sometimes in different limbs, for example, the knee and hip on one limb.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a real problem of modern rheumatology. Extra-articular disease also spreads to internal organs and muscles. The disease develops symmetrically on both arms or legs. The disease often leads to disability.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects the connective tissues of the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems, the joints of the knees, elbows, ankles, and the heart itself. Locally, the disease can affect a person's organs and internal systems. The disease needs to be treated promptly. If this is not done, then there will be complications with fatal outcome.
Main difference
People with the disease visit their doctor with complaints of joint discomfort, pain, and limited mobility. The symptoms of arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are similar, but there are distinct differences.
arthritis changes:
- synovial membrane has fluid, joint capsule is inflamed;
- heat;
- redness in the painful area;
- pain in two joints at the same time;
- no joint deformity.
Cartilage inflammation begins with an infection, injury, or metabolic disorder.
Physiology of joint disease:
- joint modification;
- cartilage tissue wears down with age;
- inflammation, swelling and redness are not observed;
- normal temperature;
- Only one joint is affected.
Illness brings suffering to a person when performing simple movements: bending, bending, straightening, raising legs or arms. The patient hardly sat on the chair, went down the stairs.
Signs and symptoms
The disease has the following general symptoms:
- difficulty walking;
- the presence of pain in the inflamed area;
- poor mobility of the problem area.
The patient's usual way of life is disturbed. Every morning, when you get out of bed, you need to "release" to go to the kitchen, control the pain.
What's more dangerous?
The disease brings a lot of pain and inconvenience to the patient.
Arthritis occurs due to inflammation in the body. He is being treated. It is important to contact a specialist promptly, not waiting for bone loss and other complications.
Osteoarthritis is a "disease of the elderly" with changes in the joints. Cartilage thins. Joint fluid, which is the source of nutrients for tissues, cannot be restored. The consequences of the disease are irreversible. To ease a person's condition it is possible that a specialist will establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Diagnose
It includes the implementation of various procedures and activities. During the examination, the doctor discovers from the arthritis patient information about past infections and injuries. Determine the course of the disease and prescribe the diagnosis:
- Blood test to detect uric acid.
- Joint ultrasound.
- X-ray of the affected area.
- CT.
- Arthroscopy.
The results show the full clinical picture of the disease.
Step-by-step diagnosis of joint disease:
- Visually, the doctor assesses joint mobility. In the problem area are areas of solidification observed, crackling is heard. What condition are the muscles around the painful joint?
- Bone growth and joint deformity make it possible to see X-rays.
- Analysis and histology of synovial fluid.
- Complete blood count.
Physical training
I would like to note that exercise therapy, swimming - effectively support in the prevention and treatment of joint diseases. Physical activity aimed at restoring joint mobility. Increased movement of blood flow in the affected area stimulates cleaning and restoration of joint tissues.
We must not forget the limitations of physical therapy exercises:
- It is done during periods of remission when there is no severe pain.
- In old age, concomitant diseases or severe deterioration of the joints do not allow performing sports exercises.
- Overweight patients are allowed to exercise a limited amount without overloading.
- The effect of occupational therapy is regular exercise, alternating with periods of rest for the joints.
Rheumatic diseases are treated by rheumatologists and orthopedic surgeons. Early diagnosis and proper treatment will allow you to live without complications. Patients who seek prompt help will have a better chance of continuing to live a normal life. With dry joints, this is a measure to relieve the condition, prevent the progression of the disease. And most importantly, don't become disabled.

























